二、单表的 CURD 操作
二、单表的 CURD 操作
CURD 操作,即指对数据库中实体对象的 增 Create、改 Update、查 Read、删 Delete 操作。
2.1 自定义 Dao 接口实现类
2.1.1 修改 Dao 接口
IStudentDao.java:增加 增 、改 、查 、删 这四个接口方法
public interface IStudentDao {
// 插入
void insertStudent(Student student);
void insertStudentCatchId(Student student);
// 删改
void deleteStudentById(int id);
void updateStudent(Student student);
// 查询所有
List<Student> selectAllStudents();
Map<String, Student> selectStudentMap();
// 查询指定学生
Student selectStudentById(int id);
// 根据姓名查询
List<Student> selectStudentsByName(String name);
}
2.1.2 实现插入后获取 id 方法
(1)修改映射文件
想在插入数据后获取其 id 的值有两种方法。
insert into student(name,age,socre) values('王五',25,95.5);
# 方法一
select @@identity;
# 方法二
select LAST_INSERT_ID();
所以利用这条语句可以在插入学生信息到数据库后,自动将学生信息的 id 初始化。故在映射文件中,加入以下代码。
- <selectKey/> 标签的 resultType 来确定执行查询语句后返回值的类型,也可以用 MyBatis 内置的类型别名。
- keyProperty 属性用于指定将返回的值 赋值 给插入对象的哪个属性,本例是初始化 id 属性,故填写 “ id "。
- order 属性决定获取 id 在 insert 语句的之前还是之后,Mysql 是先插入用户填的数据再生成 id,Oracle 是先生成 id 再插入数据。
<insert id="insertStudentCatchId">
insert into student(name,age,score) values (#{name},#{age},#{score})
<selectKey resultType="int" keyProperty="id" order="AFTER">
select @@identity
</selectKey>
</insert>
(2)修改 Dao 实现类
无需大修改,只需要把之前插入的复制过来,并改变调用的方法。
@Override
public void insertStudentCatchId(Student student) {
try {
sqlSession=MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();
// 修改的地方
sqlSession.insert("insertStudentCatchId", student);
sqlSession.commit();
}finally {
if(sqlSession!=null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
(3)修改测试类
测试类需要测试 id 属性是否在插入数据后被初始化了。
@Test
public void test02() {
Student student = new Student("张三", 23, 93.5);
System.out.println("插入前:"+student);
dao.insertStudentCatchId(student);
System.out.println("插入后:"+student);
}
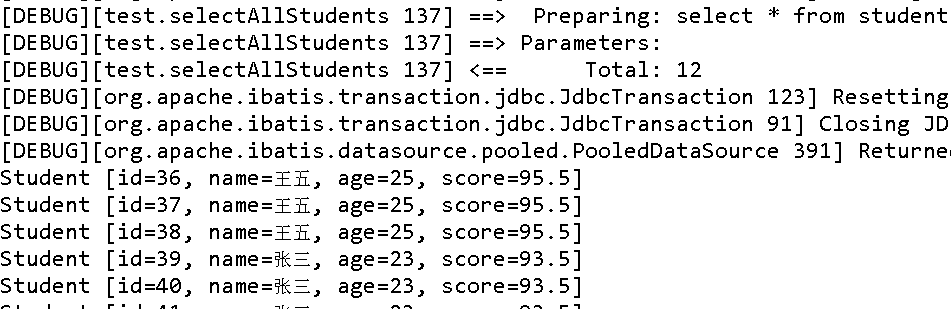
日志输出结果如下,可以看见 id 属性被初始化了

2.1.3 删除数据
(1)修改映射文件
Sql语句中的 “ #{ } " 中的标识为占位符,会将传进来的值填入该位置。因为只有一个参数传进来,所以大括号里填什么都可以。
<delete id="deleteStudentById">
delete from student where id=#{xxx}
</delete>
(2)修改 Dao 实现类
@Override
public void deleteStudentById(int id) {
try {
sqlSession=MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();
// 修改的地方
sqlSession.delete("deleteStudentById", id);
sqlSession.commit();
}finally {
if(sqlSession!=null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
(3)修改测试类
@Test
public void test03() {
dao.deleteStudentById(35);
}
2.1.4 修改数据
(1)修改映射文件
这里 ” #{ } “ 符号里的内容,必须是传进来对象的属性名,不能随意填写。
<update id="updateStudent">
update student set name=#{name}, age=#{age}, score=#{score}
where id=#{id}
</update>
(2)修改 Dao 实现类
@Override
public void updateStudent(Student student) {
try {
sqlSession=MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();
// 修改的地方
sqlSession.update("updateStudent", student);
sqlSession.commit();
}finally {
if(sqlSession!=null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
(3)修改测试类
这里因为用于测试,所以自定义了一个 student 对象来执行更新操作。
@Test
public void test04() {
Student student = new Student("李四", 23, 93.5);
student.setId(45);
dao.updateStudent(student);
}
2.1.5 查询所有对象-返回 List
(1)修改映射文件
resultType 属性表明在数据库查出的每一条记录,封装成的 类型。如果主配置文件配置的别名,这里则可以使用别名。
<select id="selectAllStudents" resultType="Student">
select * from student
</select>
(2)修改 Dao 实现类
用 List 来接收执行语句后返回的结果。因为不需要修改数据库的数据,所以不需要提交。
@Override
public List<Student> selectAllStudents() {
List<Student> students = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();
// 修改的地方
students = sqlSession.selectList("selectAllStudents");
// sqlSession.commit();
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
return students;
}
(3)修改测试类
将接收到的 List 用 ForEach 语句进行输出,查看结果。
@Test
public void test05() {
List<Student> students = dao.selectAllStudents();
for(Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
2.1.6 查询所有对象-返回 Map
(1)修改映射文件
映射文件不用修改
(2)修改 Dao 实现类
使用 selectMap( String statement, String mapKey ) 方法。
- 在这个方法执行的时候,对将每条记录封装成指定对象,然后作为 Map 的 value;
- 然后的第二个参数是指定以对象的哪一个属性作为 Map 的 key,因为 Map 种的 key 是唯一的,所以若 key 的属性值在 DB 中不唯一,则后面查询到的值会覆盖前面的值,即查询到的一定是 DB 中该同名属性值的最后一条记录;
- 这里为了输出全部学生信息,所以第二个参数填写 “ id ”。
@Override
public Map<Integer, Student> selectStudentMap() {
Map<Integer, Student> studentsMap = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();
// 修改的地方
studentsMap = sqlSession.selectMap("selectAllStudents", "id");
// sqlSession.commit();
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
return studentsMap;
}
(3)修改测试类
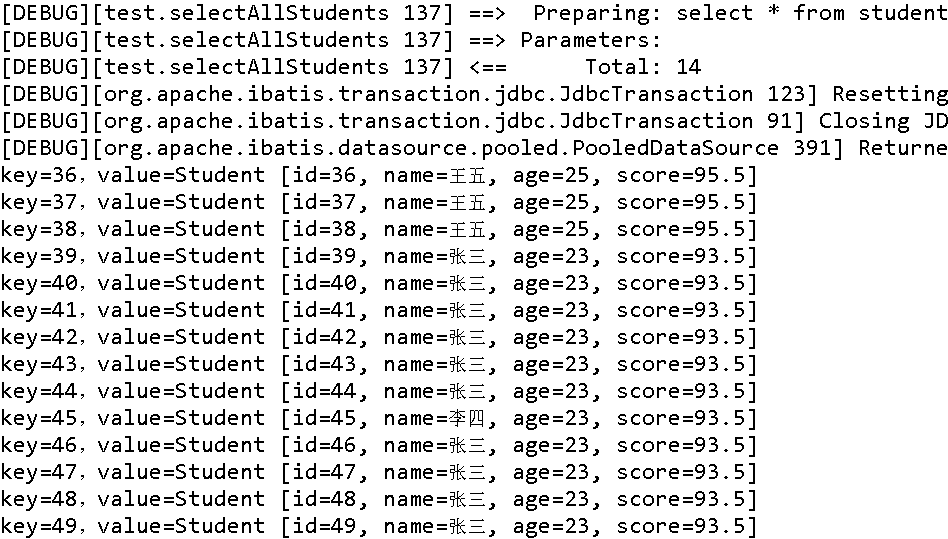
在测试类中,接收 Map 后逐个输出。Map 输出有四种。
参考 java中Map遍历的四种方式(博客园)
- 第一种方法:在for循环中使用entries实现Map的遍历;
- 第二种方法:在for循环中遍历key或者values,一般适用于只需要map中的key或者value时使用;
- 第三种方法:通过Iterator遍历;
- 第四种方法:通过键找值遍历,这种方式的效率比较低,因为本身从键取值是耗时的操作。
@Test
public void test06() {
Map<Integer, Student> studentsMap = dao.selectStudentMap();
// 第一种方法:在for循环中使用entries实现Map的遍历
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Student> entry : studentsMap.entrySet()){
Integer mapKey = entry.getKey();
Student mapValue = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("key="+mapKey+",value="+mapValue);
}
/*
* 第二种方法:在for循环中遍历key或者values,一般适用于只需要map中的key或者value时使用
* 输出 key
* for(Integer key : studentsMap.keySet()){ System.out.println(key); }
* 输出 value
* for(Student value : studentsMap.values()){ System.out.println(value);
* }
*/
/*
* 第三种方法:通过Iterator遍历
* Iterator<Entry<Integer, Student>> entries = studentsMap.entrySet().iterator();
* while(entries.hasNext()){
* Entry<Integer,Student> entry = entries.next();
* Integer key = entry.getKey();
* Student value = entry.getValue();
* System.out.println(key+":"+value); }
*/
/*
* 第四种方法:通过键找值遍历,这种方式的效率比较低,因为本身从键取值是耗时的操作
* for(Integer key : studentsMap.keySet()){
* Student value = studentsMap.get(key);
* System.out.println(key+":"+value); }
*/
}
输出结果如下:
2.1.7 查询单个对象
(1)修改映射文件
因为传进来的值只有一个,所以 " #{ } " 里的值可以任意填写。
<select id="selectStudentById" resultType="Student">
select * from student where id=#{jjj}
</select>
(2)修改 Dao 实现类
@Override
public Student selectStudentById(int id) {
Student student=null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();
// 修改的地方
student = sqlSession.selectOne("selectStudentById", id);
// sqlSession.commit();
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
return student;
}
(3)修改测试类
@Test
public void test07() {
Student student = dao.selectStudentById(44);
System.out.println(student);
}
2.1.8 模糊查询
(1)修改映射文件
在进行模糊查询时,需要进行字符串的拼接。SQL 中的字符串的拼接使用的是 函数 concat(arg1, arg2, ...) 或者直接以 空格 间隔。这两种都是以 动态参数 的形式出现在SQL语句中的。

还可使用如下方式,只是需要注意,“ ${ } ” 符号中只能填写 value,不能使用其它。这种方式是纯粹的 字符串拼接 ,直接将参数拼接到了 SQL 语句中。这种方式可能会 发生 SQL 注入。

<select id="selectStudentsByName" resultType="Student">
<!-- 这两种是以动态参数填写到 SQL 语句中
select * from student where name like concat('%',#{ooo},'%')
select * from student where name like '%' #{ooo} '%' -->
<!-- 这种方式是单纯的字符串拼接 -->
select * from student where name like '%${value}%'
</select>
(2)修改 Dao 实现类
@Override
public List<Student> selectStudentsByName(String name) {
List<Student> students;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();
// 修改的地方
students = sqlSession.selectList("selectStudentsByName", name);
sqlSession.commit();
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
return students;
}
(3)修改测试类
@Test
public void test08() {
List<Student> students = dao.selectStudentsByName("王");
for(Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
2.2 属性名与字段名不一致的解决
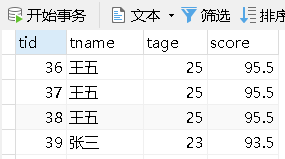
2.1.1 修改 Student 表
修改了前三个字段名,最后一个 sroce 字段没有修改
2.1.2 修改映射文件
修改 selectStudentById 的 SQL 语句
<select id="selectStudentById" resultType="Student">
<!-- 之前的 SQL 语句
select id,name,age,score from student where id=#{jjj} -->
<!-- 现在的 SQL 语句 -->
select tid,tname,tage,score from student where tid=#{jjj}
</select>
2.1.3 直接运行
若直接运行,不会报错,但输出接收数据的对象,会发现部分的属性是空的。
根据日志可知,查出了结果。
所以是将查询结果 映射 到对象的对应属性出现了问题。

2.1.4 使用别名
使用别名,修改起来简单但修改的数量多的时候会比较麻烦。
<select id="selectStudentById" resultType="Student">
<!-- 之前的 SQL 语句
select tid,tname,tage,score from student where id=#{jjj} -->
<!-- 现在的 SQL 语句 -->
select tid id,tname name,tage age,score from student where tid=#{jjj}
</select>
2.1.5 使用结果映射 resultMap
将 resultType 属性改成 resultMap 属性,因为要将查询出来的结果交给 <resultMap/> 标签进行映射处理,再进行封装,其属性值为指定的 resultMap 的 id 属性。
<select id="selectStudentById" resultMap="studentMapper">
select tid,tname,tage,score from student where tid=#{jjj}
</select>
- 使用了<resultMap/> 标签的两个属性;
- type 属性定义封装对象的类型;
- id 属性用于标识该标签。
- <id/> 标签用于指定封装对象主键的映射,<result/> 标签用于指定其他字段名的映射,用到了它们的两个属性。
- column 属性填写数据库的字段名;
- property 属性填写对象的属性名。
<resultMap type="Student" id="studentMapper">
<id column="tid" property="id"/>
<result column="tname" property="name"/>
<result column="tage" property="age"/>
</resultMap>
2.3 Mappper 动态代理
在前面例子中自定义Dao接口实现类时发现一个问题:Dao 的实现类其实并没有干什么实质性的工作。它仅仅就是通过 SqlSession 的相关 API 定位到映射文件 mapper 中相应 id 的 SQL 语句,真正对 DB 进行操作的工作其实是由框架通过 mapper 中的 SQL 完成的。
所以,MyBatis 框架可以抛开了 Dao 的实现类,直接定位到映射文件 mapper 中的相应 SQL 语句,对 DB 进行操作。这种对 Dao 的实现方式称为 **Mapper 的动态代理方式 **。
Mapper动态代理方式 无需 程序员实现Dao接口。接口是由MyBatis结合映射文件 自动 生成的动态代理实现的。
注:以下例子已将数据库的字段名还原成 id,name,age,score。
2.3.1 映射文件的 namespace
一般情况下,一个Dao接口的实现类方法使用的是同一个SQL映射文件中的SQL映射id。所以,MyBatis框架要求,将映射文件中 <mapper/> 标签的 namespace属性设为 Dao 接口的全类名,则系统会根据方法所属的 Dao 接口,自动到对应的 namespace 的映射文件中查找对应的 SQL 标签映射。
简单来说,通过接口名即可定位到映射文件mapper。
先将 StudentDaoImpl.java 文件删除,然后将 <mapper/> 标签的 namespace 属性改成以下代码。
<mapper namespace="com.hahg.dao.IStudentDao" >
2.3.2 Dao 接口方法名
MyBatis 框架要求,接口中的方法名,与映射文件中相应的 SQL 标签的 id 值相同。系统会自动根据方法名到相应的映射文件中查找同名的 SQL 映射 id。
简单来说,通过方法名就可定位到映射文件 mapper 中相应的 SQL 语句,所以接口名与 id 值相同。
2.3.3 Dao 对象的获取
使用时,只需在 @Before 注解方法中调用 SqlSession 的 getMapper( Class<T> type ) 方法,即可获取指定接口的实现类对象。该方法的参数为指定 Dao 接口类的 class 值。
@Before
public void before() {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();
dao = sqlSession.getMapper(IStudentDao.class);
}
2.3.4 添加细节
(1)添加 @After 注解方法
在 @After 注解方法中关闭 SqlSession 对象。
@After
public void after() {
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
(2)添加提交方法
在 增、删、改 测试方法的最后,添加上 SqlSession 的 commit() 方法,完成提交。
@Test
public void test01() {
Student student = new Student("张三", 23, 93.5);
dao.insertStudent(student);
// 添加的 commit() 方法
sqlSession.commit();
}
@Test
public void test02() {
Student student = new Student("张三", 23, 93.5);
System.out.println("插入前:" + student);
dao.insertStudentCatchId(student);
// 添加的 commit() 方法
sqlSession.commit();
System.out.println("插入后:" + student);
}
(3)删除 selectStudentMap 方法
MyBatis框架对于 Dao 查询的自动实现,底层 只会调用 selectOne 与 selectList 方法。而框架选择方法的标准是测试类中用于接收返回值的对象类型。
若接收类型为 List,则自动选择 selectList 方法;否则,自动选择 selectOne 方法。
这里接收类型为 Map,所以框架选择了 selectOne 方法,会报错。所以这里需要删除这个selectStudentMap()方法的测试
2.3.5 多查询条件无法整体接收问题的解决
在实际使用中,表单中所给出的查询条件有时是 无法将其封装为一个对象的,也就是说,查询方法只能携带多个参数,而不能携带将这多个参数进行封装的一个对象。对于这个问题,有两种解决方案。
(1)封装成 Map
将这多个参数封装为一个Map<String, Object>,在 SQL 语句中提取 Map 的值。
A、修改Dao接口
在Dao接口中添加如下方法:
List<Student> selectStudentsByMap(Map<String,Object> map);
B、修改测试类
在测试类中定义一个 HashMap ,里面存放查找数据的条件,并用 List 接收查询出来的结果。
@Test
public void test06() {
Map<String, Object> map= new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("nameCondition", "张");
map.put("ageCondition", 23);
List<Student> students = dao.selectStudentsByMap(map);
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
C、修改映射文件
" #{ } " 符号里面填的是 Map 的 key 值。
<select id="selectStudentsByMap" resultType="Student">
select * from student
where name like '%' #{nameCondition} '%'
and age > #{ageCondition}
</select>
(2)多个参数逐个接收
对于 mapper 中的 SQL 语句,可以通过参数索引 “ #{ index } ” 的方式逐个接收每个参数。
index 可以有两种形式填写
- arg0 为第一个参数,arg1 为第二个参数,argx 为第 x+1 个参数
- param1 为第一个参数,param2 为第二个参数,paramx 为第 x 个参数
A、修改Dao接口
List<Student> selectStudentsByConditions(String name, int age);
B、修改测试类
将 “ 张 ” 作为第一个参数,23 作为第二个参数
@Test
public void test07() {
List<Student> students = dao.selectStudentsByConditions("张",23);
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
C、修改映射文件
<select id="selectStudentsByConditions" resultType="Student">
select * from student
where name like '%' #{param1} '%'
and age > #{param2}
</select>
2.4动态SQL
动态 SQL ,主要用于解决查询条件不确定的情况:在程序运行期间,根据用户提交的查询条件进行查询。
提交的查询条件不同,执行的 SQL 语句不同。若将每种可能的情况均逐一列出,对所有条件进行排列组合,将会出现大量的SQL语句。
此时,可使用动态 SQL 来解决这样的问题。动态 SQL,即通过 MyBatis 提供的各种标签对条件作出判断以实现动态拼接 SQL 语句。
这里的条件判断使用的表达式为 OGNL 表达式。常用的动态 SQL 标签有 <if/>、<where/>、<choose/>、<foreach>等。
2.4.1 <if/> 标签
需求:
- 只输入 age ,就只查询年龄大于该数字的学生信息;
- 只输入 name ,就只查询名字有该字符的学生信息;
- 若两个都输入,则查询年龄大于该数字且名字有该字符的学生信息;
- 若都不输入,则查询所有学生信息。
对于该标签的执行,当test的值为true时,会将其包含的SQL片断拼接到其所在的SQL语句中。这引发的问题是,查询条件不确定,查询条件依赖于用户提交的内容。此时,就可使用动态SQL语句,根据用户提交内容对将要执行的 SQL 进行拼接。
(1)定义 Dao 接口
这里便于测试,所以形参的类型为 Student,便于在 Sql 语句中提取数据。
List<Student> selectStudentsIf(Student student);
(2)定义映射文件
- 第 3 ~ 5 行,实现若姓名不为空,则进行模糊查询;
- 第 6 ~ 8 行,实现若年龄不为空,则按要求查询;
- where 1 = 1,用于实现两个条件都不满足时查询所有信息;
注意
动态 Sql 中 test 的值,建议将 > 、>= 等符号替换成实体符号。特别是 < 符号,出现就会报错。
| 原符号 | < | <= | > | >= | & | ' | " |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 替换符号 | < | <= | > | >= | & | ' | " |
<select id="selectStudentsIf" resultType="Student">
select * from student where 1=1
<if test="name!=null and name!=''">
and name like '%' #{name} '%'
</if>
<if test="age>0">
and age > #{age}
</if>
</select>
(3)修改测试类
@Test
public void test01() {
/*
* 两个条件都有
* Student student = new Student("张",23,93.5);
* 只有姓名
* Student student = new Student("张",0,93.5);
* 只有年龄
* Student student = new Student("",23,93.5);
*/
// 两个都没有
Student student = new Student("",0,93.5);
List<Student> students = dao.selectStudentsIf(student);
for (Student stu : students) {
System.out.println(stu);
}
}
2.4.2 <where/> 标签
由上可知,在 where 后,需要添加永为真子句 1=1。当数据量很大时,每查询一条语句就会判断一次 1=1,这样会严重影响查询效率。所以可以使用 <where/> 标签来解决。
(1)修改 Dao 接口
List<Student> selectStudentsWhere(Student student);
(2)修改映射文件
只需要将 “ where 1=1 ” 替换成 <where/> 标签。
该标签的作用是,在有查询条件时会自动加上 " where " ;在没有查询条件时,就不会加上 " where " 。系统在解析 Sql 语句中,会将语句多余的 and 删除。所以第 5 行的 “ and ”,可以加上,可以删除。
<select id="selectStudentsWhere" resultType="Student">
select * from student
<where>
<if test="name!=null and name!=''">
and name like '%' #{name} '%'
</if>
<if test="age>0">
and age > #{age}
</if>
</where>
</select>
(3)修改测试类
@Test
public void test02() {
/*
* 两个条件都有
* Student student = new Student("张",23,93.5);
* 只有姓名
* Student student = new Student("张",0,93.5);
* 只有年龄
* Student student = new Student("",23,93.5);
*/
// 两个都没有
Student student = new Student("",0,93.5);
List<Student> students = dao.selectStudentsWhere(student);
for (Student stu : students) {
System.out.println(stu);
}
}
- 两个条件都没有的输出结果:
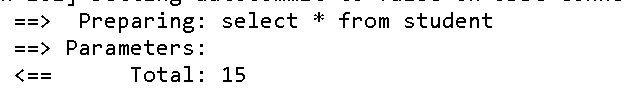
- 有查询条件的输出结果:

2.4.3 <choose/> 标签
需求:
- 若姓名不为空,则只查询姓名;
- 若姓名为空,则只查询年龄;
- 若两个都为空,则不查询任何信息。
(1)修改 Dao 接口
List<Student> selectStudentsChoose(Student student);
(2)修改映射文件
该标签会从第一个 <when/> 标签进行判断,若 <when/> 标签的 test 属性值为 true 则退出 <choose/> 标签,若所有 <when/> 标签的 test 属性值都为 false ,则最后会执行 <otherwise/> 标签。
简单来说,就像 Java 的 IF - Else IF - Else 语句。
<select id="selectStudentsChoose" resultType="Student">
select * from student
<where>
<choose>
<when test="name!=null and name!=''">
and name like '%' #{name} '%'
</when>
<when test="age>0">
and age > #{age}
</when>
<otherwise>
1 != 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
(3)修改测试类
@Test
public void test03() {
// 两个条件都有
// Student student = new Student("张", 23, 93.5);
// 只有姓名
// Student student = new Student("张",0,93.5);
// 只有年龄
// Student student = new Student("",23,93.5);
// 两个都没有
Student student = new Student("",0,93.5);
List<Student> students = dao.selectStudentsChoose(student);
for (Student stu : students) {
System.out.println(stu);
}
}
2.4.4 <foreach/> 标签-遍历数组
需求:查询以数组存储的 id 值的学生信息。
(1)修改 Dao 接口
List<Student> selectStudentsForeachArray(Object[] studentIds);
(2)修改映射文件
Sql 语句查询条件为一组数据时,使用 “ 字段名 in (a, b, c) "
- 先 用 <if/> 标签判断数组是否为空。数组在 MyBatis 的内置别名为 array,所以用 array 表示传进来的数组。
- 用到了 <foreach/> 标签的 5 个属性:
- collection 指定遍历的容器类型;
- open 和 close 指定开始和结束符号;
- item 指定数组中取出来的每一个元素的名字;
- separator 以什么符号分隔;
<select id="selectStudentsForeachArray" resultType="Student">
<!-- select * from student where id in (1,2,3) -->
select * from student
<if test="array != null and array.length != 0">
where id in
<foreach collection="array" open="(" close=")" item="myid"
separator=",">
#{myid}
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
除了 array,MyBatis还有更多内置的类型别名:
基本类型:
| 别名 | 类型 | 别名 | 类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| _int | int | _integer | int |
| _short | short | _long | long |
| _double | double | _float | float |
| _byte | byte | _boolean | boolean |
常用包装类型:
| 别名 | 类型 | 别名 | 类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| string | String | byte | Byte |
| long | Long | short | Short |
| int | Integer | integer | Integer |
| double | Double | float | Float |
| boolean | Boolean | date | Date |
| object | Object | collection | Collection |
| list | List | arrayList | ArrayList |
| map | Map | hashMap | HashMap |
| iterator | Iterator | array | 数组 |
(3)修改测试类
@Test
public void test03() {
Object[] studentIds= {41,42};
List<Student> students = dao.selectStudentsForeachArray(studentIds);
for (Student stu : students) {
System.out.println(stu);
}
}
2.4.4 <foreach/> 标签-遍历基本类型的List
需求:查询以 List 存储的 id 值的学生信息。
(1)修改 Dao 接口
List<Student> selectStudentsForeachList(List<Integer> studentIds);
(2)修改映射文件
只需要将 array 换成 list 即可,需要注意的是 list 的长度属性不是 length 而是 size。
<select id="selectStudentsForeachList" resultType="Student">
<!-- select * from student where id in (1,2,3) -->
select * from student
<if test="list != null and list.size != 0">
where id in
<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" item="myid"
separator=",">
#{myid}
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
(3)修改测试类
@Test
public void test04() {
List<Integer> studentIds=new ArrayList<Integer>();
studentIds.add(41);
studentIds.add(42);
List<Student> students = dao.selectStudentsForeachList(studentIds);
for (Student stu : students) {
System.out.println(stu);
}
}
2.4.5 <foreach/> 标签-遍历泛型的List
(1)修改 Dao 接口
使用 Student 作为泛型的类型,取出 List 中的各个 Student 对象的 id 值作为查询条件。
List<Student> selectStudentsForeachList(List<Student> studentIds);
(2)修改映射文件
只需要将 item 的值更改(只是便于可读),并将值中的 id 属性取出来。
<select id="selectStudentsForeachList2" resultType="Student">
<!-- select * from student where id in (1,2,3) -->
select * from student
<if test="list != null and list.size != 0">
where id in
<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" item="stu"
separator=",">
#{stu.id}
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
(3)修改测试类
新建两个 Student 对象,并赋值 id 属性并封装成 List 。
@Test
public void test05() {
Student stu1=new Student();
stu1.setId(41);
Student stu2=new Student();
stu2.setId(42);
List<Student> students=new ArrayList<Student>();
students.add(stu1);
students.add(stu2);
List<Student> studentsList = dao.selectStudentsForeachList2(students);
for (Student stu : studentsList) {
System.out.println(stu);
}
}
2.4.6 <sql/> 标签
<sql/> 标签用于定义 Sql 片段,以便于其他 Sql 标签复用。而其他标签使用该 Sql 片段,需要使用 <include/> 标签。<sql/> 标签可以定义 Sql 语句中的任何部分。类似 Jsp 的代码块 ” <% 代码块 %> “。
优点:便于统一修改;缺点:可读性下降
(1)修改映射文件
在上例的基础上,进行修改。
- 第 1 ~ 3 行,定义 Sql 片段。
- 第 7 行,使用 <include/> 标签将片段插入进去。
<sql id="selectHead">
select * from student
</sql>
<select id="selectStudentsForeachList2" resultType="Student">
<!-- select * from student where id in (1,2,3) -->
<include refid="selectHead"/>
<if test="list != null and list.size != 0">
where id in
<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" item="stu"
separator=",">
#{stu.id}
</foreach>
</if>
</select>